Revolutionary Leap: 5 Key Aspects of the Autonomous Retail Store Revolution
Related Articles: Revolutionary Leap: 5 Key Aspects of the Autonomous Retail Store Revolution
- Revolutionary Smart Fabrics: 5 Key Innovations Transforming Textiles
- Revolutionary Biohacking: 5 Powerful Ways Tech Is Transforming Biology
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Revolutionary Leap: 5 Key Aspects of the Autonomous Retail Store Revolution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Revolutionary Leap: 5 Key Aspects of the Autonomous Retail Store Revolution
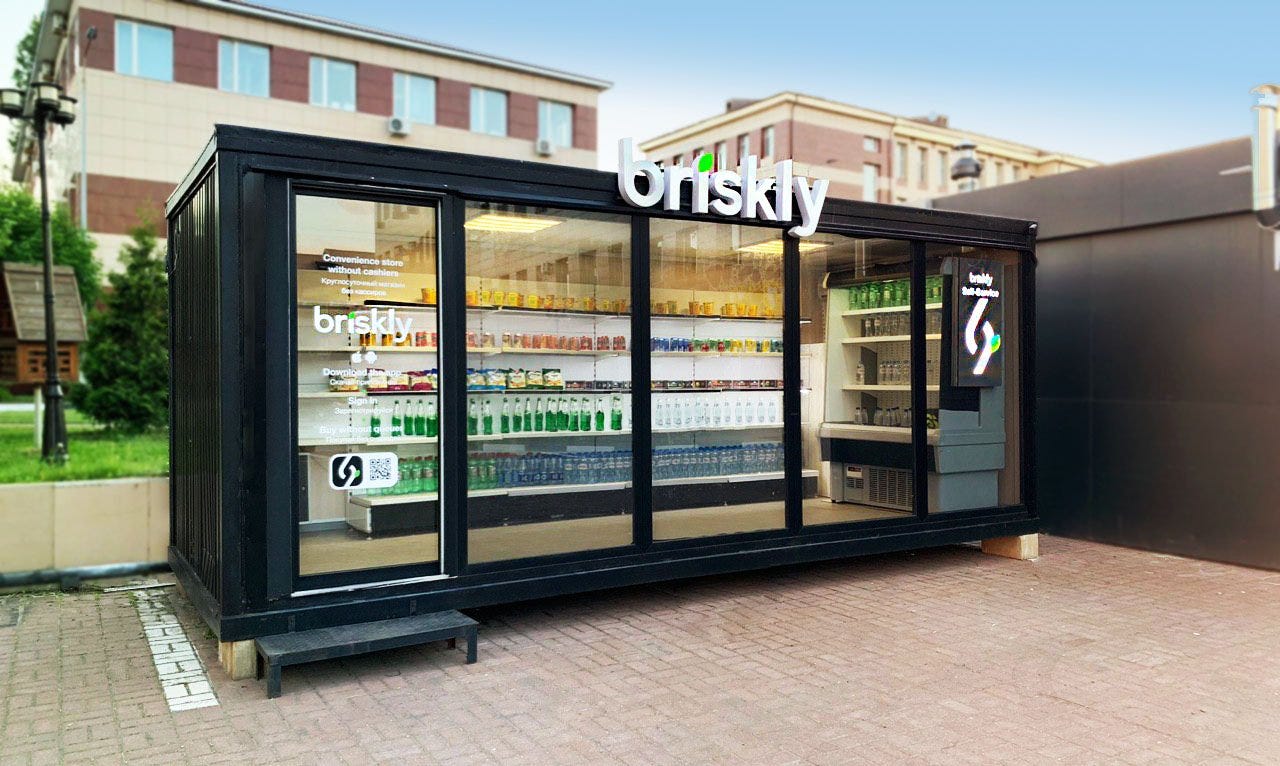

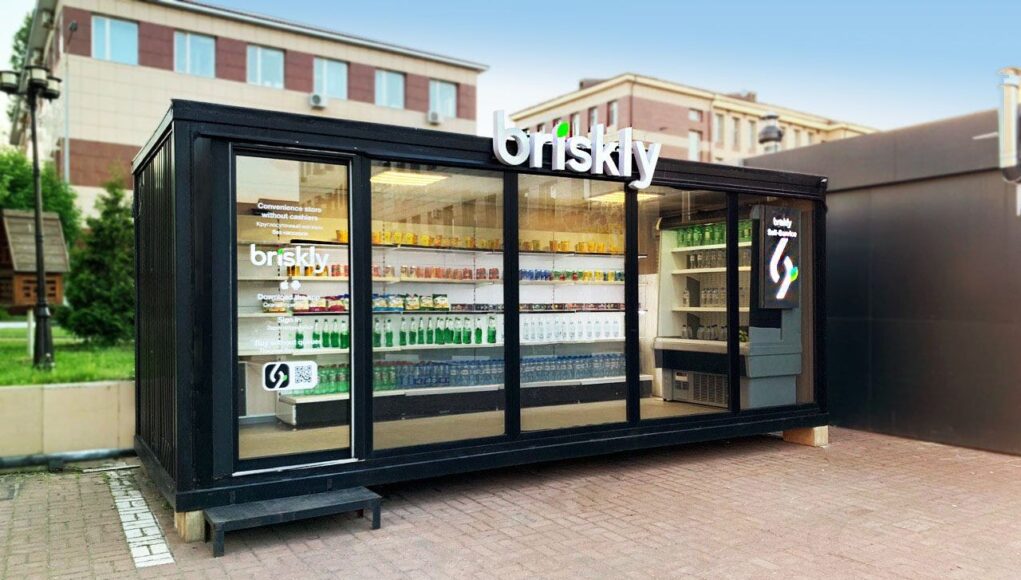
The rise of autonomous retail stores represents a monumental shift in the landscape of commerce. These cashier-less, technology-driven establishments promise a seamless and personalized shopping experience, but their implementation presents a complex tapestry of technological, logistical, and societal challenges. This article will delve into five key aspects of this revolution, exploring the innovative technologies driving the change, the operational complexities involved, the evolving consumer response, the ethical considerations arising from data collection, and the potential future of this disruptive retail model.
1. Technological Marvels: The Engine of Autonomous Retail
The heart of any autonomous retail store lies in its sophisticated technological infrastructure. This intricate system relies on a convergence of several key technologies working in harmony:
-
Computer Vision: This is arguably the most crucial component. Sophisticated algorithms analyze video feeds from strategically placed cameras throughout the store, identifying shoppers, tracking their movements, and recognizing the items they pick up and put back. This requires incredibly powerful processing capabilities to handle the real-time analysis of vast amounts of visual data, ensuring accuracy and speed. Advances in deep learning and neural networks have been instrumental in improving the accuracy and robustness of these systems, minimizing errors associated with occlusion (items being partially hidden) and lighting variations.
-
Sensor Fusion: Computer vision alone is not enough. Autonomous stores often integrate various sensor technologies to create a comprehensive understanding of the shopping environment. This includes weight sensors embedded in shelves to detect when an item is removed, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags attached to products to track their movement precisely, and even 3D cameras providing a more complete spatial awareness of the store layout and shopper interactions. The fusion of data from these diverse sensors enhances the accuracy and reliability of the inventory tracking and purchase detection systems.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are the brains behind the operation. They are responsible for processing the data from various sensors, making real-time decisions about purchases, managing inventory, and identifying potential issues like theft or equipment malfunctions. These systems continuously learn and improve their accuracy based on the data they collect, adapting to changing conditions and improving the overall efficiency of the store. The algorithms used are incredibly complex, requiring significant computational power and specialized expertise to develop and maintain.

Edge Computing: Processing all the data generated by an autonomous store in the cloud would introduce significant latency, leading to delays and inaccuracies. Therefore, a significant portion of the processing is handled at the "edge," meaning on-site within the store itself. This reduces the reliance on cloud connectivity and ensures real-time responses, crucial for a smooth shopping experience. This requires robust and reliable on-site computing infrastructure capable of handling the immense data flow.
-
Secure Payment Systems: A seamless checkout experience is paramount. Autonomous stores typically integrate mobile payment systems, allowing shoppers to pay using their smartphones without the need for a traditional checkout process. This requires secure integration with various payment gateways and robust security measures to protect sensitive customer data. Biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition, are also being explored to further streamline the payment process.
2. Operational Challenges: Navigating the Complexities
Despite the technological advancements, implementing and operating autonomous retail stores presents significant operational challenges:
-
Accuracy and Error Handling: While technology has advanced significantly, errors can still occur. False positives (incorrectly identifying a purchase) and false negatives (missing a purchase) can lead to inventory discrepancies and customer dissatisfaction. Robust error handling mechanisms are crucial, including manual override options and processes to address discrepancies.

Maintenance and Upkeep: The complex technological infrastructure requires regular maintenance and updates. This necessitates skilled technicians and ongoing investment in software and hardware. Downtime due to technical malfunctions can severely disrupt operations and impact customer experience.
-
Security Concerns: The absence of human cashiers raises concerns about theft and shoplifting. While technology can detect some forms of theft, it’s not foolproof. Strategies to deter theft, such as improved surveillance systems and advanced security protocols, are essential.
-
Scalability and Cost: Implementing autonomous retail technology is expensive. The initial investment in hardware, software, and integration is substantial. Scaling the technology to a larger number of stores requires significant capital expenditure and logistical planning.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating autonomous retail technology with existing supply chain management systems and inventory control processes can be challenging. Seamless data flow between the store’s technology and the broader business operations is vital for efficient inventory management and overall business success.
3. Consumer Adoption: A Gradual Embrace
Consumer acceptance of autonomous retail is gradually increasing, but it’s not without its reservations. Many consumers initially express concerns about privacy, the accuracy of the technology, and the lack of human interaction. However, the convenience and speed of the cashier-less experience are significant attractions. Successful implementation requires addressing these concerns through transparent data policies, robust error handling, and effective communication with consumers. Positive user experiences and word-of-mouth marketing are crucial for driving broader adoption.
4. Ethical Considerations: Data Privacy and Surveillance
The data collected by autonomous retail stores raises significant ethical considerations, particularly concerning privacy. The constant monitoring of shopper behavior raises concerns about surveillance and the potential for misuse of personal data. Transparent data policies, clear communication about data usage, and robust data security measures are essential to build consumer trust and address these concerns. Regulations and guidelines regarding data privacy in the context of autonomous retail are still evolving, and businesses must proactively address these ethical challenges.
5. The Future of Autonomous Retail: A Vision of Personalized Commerce
The future of autonomous retail is bright, promising a more personalized and efficient shopping experience. Further technological advancements will lead to more accurate, reliable, and seamless operations. Integration with other technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), could create immersive and engaging shopping experiences. The potential for personalized recommendations, targeted promotions, and customized product offerings based on individual shopper data is immense. However, responsible implementation, addressing ethical concerns, and ensuring consumer trust will be crucial for realizing the full potential of this revolutionary retail model. The future likely involves a hybrid model, combining the efficiency of autonomous technology with the human touch where needed, creating a truly optimized retail experience. The journey towards widespread adoption will require continuous innovation, careful planning, and a keen understanding of the evolving needs and preferences of consumers. Ultimately, the success of autonomous retail depends on its ability to provide a superior shopping experience while upholding ethical standards and respecting consumer privacy.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Revolutionary Leap: 5 Key Aspects of the Autonomous Retail Store Revolution. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
google.com