Revolutionary 5 Ways Tech is Transforming Healthcare
Related Articles: Revolutionary 5 Ways Tech is Transforming Healthcare
- Revolutionary Blockchain: 5 Powerful Applications Beyond Crypto
- Amazing Breakthrough: 5 Revolutionary Transformative Wearable Technologies
- Advancements In Green Tech Solutions
- 7 Amazing Smart Cities Revolutionizing Urban Life
- 10 Crucial Ethical Dilemmas: Unmasking AI’s Shadow Power
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Revolutionary 5 Ways Tech is Transforming Healthcare. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Revolutionary 5 Ways Tech is Transforming Healthcare

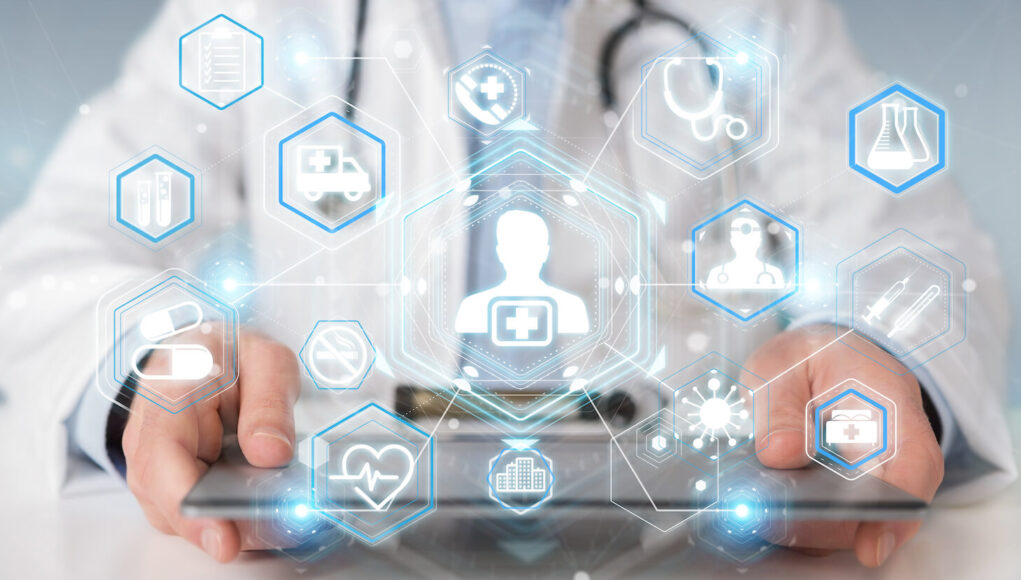
Technology’s impact on healthcare is nothing short of revolutionary. It’s reshaping how we diagnose illnesses, administer treatment, manage patient data, and even interact with medical professionals. This transformative power is evident across various sectors, promising a future of more efficient, accessible, and personalized healthcare for everyone. However, this rapid advancement also presents challenges that require careful consideration and proactive solutions. This article explores five key areas where technology is fundamentally altering the healthcare landscape, highlighting both the incredible potential and the inherent complexities.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Diagnosis and Treatment:
AI and ML are rapidly becoming indispensable tools in healthcare, significantly improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. AI algorithms can analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) with remarkable speed and precision, often identifying subtle anomalies that might be missed by the human eye. This is particularly crucial in detecting cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and other life-threatening conditions at their early stages, when treatment is most effective. Radiologists, for example, are increasingly using AI-powered tools to assist in their work, improving diagnostic speed and reducing workload.
Furthermore, AI is being integrated into various treatment modalities. In oncology, AI algorithms can analyze patient data – including genetic information, medical history, and tumor characteristics – to predict treatment response and personalize cancer therapies. This precision medicine approach minimizes side effects and maximizes the chances of successful treatment. Similarly, in cardiology, AI is helping predict heart attacks and strokes, enabling proactive interventions and preventative care.
However, the widespread adoption of AI in healthcare is not without its challenges. Concerns regarding data privacy and security are paramount. The vast amounts of sensitive patient data used to train and operate AI algorithms need robust protection against unauthorized access and breaches. Furthermore, the "black box" nature of some AI algorithms – where it’s difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions – raises concerns about transparency and accountability. Ensuring the fairness and equity of AI algorithms is also crucial, as biases in the data used to train these systems can lead to disparities in healthcare access and outcomes. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving stringent regulatory frameworks, ethical guidelines, and rigorous testing and validation of AI algorithms.
2. Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring:
The rise of telemedicine has dramatically expanded access to healthcare, particularly for individuals in remote areas or those with limited mobility. Virtual consultations, remote monitoring of vital signs, and online prescription refills are becoming increasingly common, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving convenience for patients. Telemedicine has proven particularly valuable during public health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, enabling healthcare providers to maintain continuity of care while minimizing the risk of infection.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) utilizes wearable sensors and other connected devices to collect and transmit patient data to healthcare professionals in real-time. This enables continuous monitoring of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, allowing for early detection of potential problems and timely interventions. RPM is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions like diabetes, heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), enabling proactive management and reducing hospital readmissions.
Despite its benefits, telemedicine faces challenges, including the digital divide – the unequal access to technology and internet connectivity – which disproportionately affects low-income communities and rural populations. Ensuring equitable access to telemedicine requires bridging this digital divide through initiatives that improve internet infrastructure and provide affordable access to technology. Furthermore, regulatory hurdles and reimbursement policies can hinder the widespread adoption of telemedicine. Clear guidelines and policies are needed to ensure the quality, safety, and reimbursement of telemedicine services.
3. Big Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling:
Healthcare generates enormous amounts of data – from electronic health records (EHRs) to genomic information and wearable sensor data. Big data analytics techniques can process and analyze this data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can improve healthcare outcomes. For instance, analyzing patient data can help identify individuals at high risk of developing certain diseases, enabling proactive interventions and preventative care. Predictive modeling can forecast hospital readmissions, allowing healthcare providers to implement strategies to reduce readmissions and improve patient outcomes.
Big data analytics also plays a crucial role in public health surveillance. Analyzing data from various sources can help identify and track outbreaks of infectious diseases, allowing public health officials to respond quickly and effectively. Furthermore, big data analytics can be used to optimize healthcare resource allocation, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and effectively to meet the needs of the population.
However, the use of big data in healthcare raises concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting patient data from unauthorized access and breaches is crucial. Furthermore, ensuring the responsible use of patient data and preventing its misuse requires robust ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks. The potential for bias in big data analyses also needs careful consideration. Biases in the data can lead to inaccurate conclusions and unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
4. Robotics and Automation in Surgery and Patient Care:

Robotics are transforming surgical procedures, enabling minimally invasive surgeries with greater precision and dexterity than traditional methods. Robotic surgery is associated with smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery times, and shorter hospital stays. Surgical robots are equipped with advanced imaging systems and instruments, providing surgeons with a magnified and high-definition view of the surgical field.
Automation is also playing an increasingly important role in patient care. Automated systems can assist with tasks such as dispensing medication, managing patient records, and monitoring vital signs. This frees up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex tasks, improving efficiency and productivity. Automated systems can also help reduce medical errors and improve patient safety.
However, the integration of robotics and automation in healthcare requires careful consideration of safety and ethical implications. Ensuring the reliability and safety of robotic systems is crucial. Furthermore, the potential displacement of human workers due to automation needs to be addressed through retraining and upskilling initiatives.
5. Blockchain Technology for Data Security and Interoperability:
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent nature, holds significant potential for enhancing data security and interoperability in healthcare. Blockchain can create a secure and immutable record of patient data, protecting it from unauthorized access and modification. This is particularly important in managing sensitive medical information, such as genetic data and electronic health records. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate the secure sharing of patient data between different healthcare providers, improving care coordination and reducing redundancies.
Blockchain can also improve the transparency and traceability of pharmaceutical supply chains, helping to combat counterfeit drugs and ensure the authenticity of medications. This is particularly crucial in preventing the distribution of substandard or falsified medicines, which can have serious health consequences.
Despite its potential, the adoption of blockchain in healthcare faces challenges. The complexity of implementing blockchain systems and the need for standardization are significant hurdles. Furthermore, concerns about scalability and the lack of regulatory clarity can hinder its widespread adoption.
In conclusion, technology is profoundly reshaping the healthcare landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve the quality, accessibility, and efficiency of healthcare services. From AI-powered diagnostics to telemedicine and blockchain-secured data management, technological advancements are revolutionizing how we diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. However, realizing the full potential of these technologies requires careful consideration of the ethical, social, and regulatory implications, ensuring equitable access and mitigating potential risks. By proactively addressing these challenges, we can harness the transformative power of technology to create a more equitable, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare system for all.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Revolutionary 5 Ways Tech is Transforming Healthcare. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
google.com